Personal VPN Security Guideline
- Objective
Virtual private network (VPN) is one of the commonly used security technologies that have been widely used in an enterprise environment for employee remote access. On the other hand, it is also applied in protecting personal online privacy and security, which is known as personal VPN services. Although it can ensure the confidentiality of data during transmission, it does not mean that VPN technology can protect information security and data privacy in every use case. This blog not only examines personal VPN services in-depth but also helps users understand the principles of VPN technology and the security features provided by personal VPN services so that this technology can be used correctly.
- The Operation Principles of Personal VPN Service
VPN technology makes use of an encryption protocol to establish a point-to-point virtual network connection (secure VPN tunnel) on the Internet. The data sent and received by client devices are encrypted and transmitted to the destination VPN server through a secure VPN tunnel to avoid the data being intercepted or eavesdropped by hackers.
Personal VPN service is a VPN connection targeted for individual users. We can refer to the following figure to further understand the basic concept of using personal VPN services.
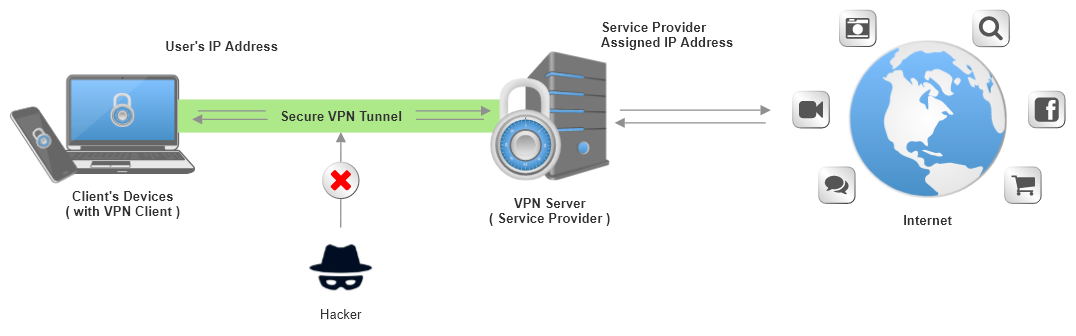
Figure 1. Personal VPN Network Diagram
The connection of the personal VPN service is divided into two parts. The first part is the point-to-point secure VPN tunnel (the green part shown in Figure 1) where the user connects to the VPN server through the VPN client in the personal device. All data transmitted through the secure VPN tunnel will be encrypted. The second part is from the VPN server to the Internet destination. Since the secure VPN tunnel (the green part in Figure 1) has been terminated in the VPN server, this transmission is not encrypted by VPN technology. When a user uses a personal VPN service, the user's data will be encrypted and transmitted to the service provider's VPN server through a secure VPN tunnel, and then transmitted to the Internet destination without encryption by the VPN technology.
In addition, when a user uses a personal VPN service, the VPN service provider will assign an IP address to the VPN client to access the Internet service. We can refer to the client device on the left of Figure 1. After the VPN client successfully connects to the personal VPN service, all data transmitted to the Internet through the personal VPN service will be changed to the IP address assigned by the service provider as the source IP address, instead of using the user's IP address.
- Use Cases for Personal VPN Services
After understanding the operating principle of personal VPN service, the following will analyse the security functions and points of attention for some use cases of personal VPN services.
3.1 Prevent Eavesdropping on Untrusted Networks
Personal VPN services are mostly used to ensure data encryption in accessing the Internet through the untrusted network, especially on free public Wi-Fi hotspots. As most public Wi-Fi hotspots have no encryption settings or lack of security measures, the data transmitted by users may be intercepted or eavesdropped. After using the personal VPN service, since the data has been encrypted, the confidentiality and integrity of the data can be ensured.
Users must note that the personal VPN service only encrypts the transmission from the client end to the VPN server (the green part in Figure 1). For the encryption from the VPN server to the Internet destination, it depends on whether the web sites or online services make use of encryption protocol (such as HTTPS) or not.
3.2 Hiding the User's IP Address
If users do not want to disclose their IP addresses on the Internet, they can achieve this purpose by using personal VPN service. When users access the Internet through the personal VPN service, the personal VPN service provider will assign the client another IP address. The Internet destination will only show the assigned IP address as the source address, instead of the user's IP address. Therefore, personal VPN services can provide anonymous Internet access services.
Users should note that personal VPN service can only hide the IP address, but not making user’s identity completely anonymous. If users reveal personal information (such as name, phone number, email, social media account, photo, etc.) while using the Internet, there are, still, chances of revealing their identities.
Users should also pay attention that, in using personal VPN services, personal VPN service providers may also retain the records of user access, such as the original IP address, assigned IP address, connection records, etc. Therefore, users should carefully choose personal VPN service providers and take their reputation and privacy policies into consideration.
3.3 Accessing to Location-Aware Online Services
If users access some location-aware online services, the service website will provide different information according to the geolocation of the IP address. Some personal VPN service providers offer VPN servers in different regions, allowing users to freely change the source IP address region to access the online services of the designated regions.
Users should note that location-aware online services may have different service terms or restrictions in different regions (e.g. some online shopping products have regional sales restrictions, etc.). In using this kind of online service, users should pay careful attention to the terms and conditions.
To summarise the above cases, the security features that personal VPN services can provide:
✓ Reduce the risk of interception or eavesdropping of data by hackers when using the Internet under the public network;
✓ Hide personal IP address in the Internet; and
✓ Change the region of source IP address via the VPN server
- Will using personal VPN services bring other security risks?
Although personal VPN services can provide the mentioned security features, hackers can still hack into the VPN server through brute force password attacks or exploiting the vulnerabilities and conduct further attacks if the VPN software is not configured correctly and appropriately or the VPN server is unpatched. On the other hand, users should carefully choose the VPN service provider. Since all user data transmission will be routed to the Internet via the VPN server, there is a chance of potential breach of users’ data if VPN service providers fail to provide proper security measures. Recently, researchers have discovered that seven Hong Kong-based VPN companies are suspected of storing customer information improperly, causing the data leakage close to 20 million users.[1]
Besides, each individual VPN service provider records users’ activities to varying degrees, and each of them has different user privacy policies. Some free service providers will collect user information and transfer it to third parties as well, such as advertising companies. Therefore, users must read their privacy policies carefully when selecting service providers. Users are recommended using "Incognito Mode" in browser to prevent the browser from recording the user's browsing behavior, thus improving the privacy of browsing the web.
Therefore, users should note that personal VPN services cannot offer the following security features:
✗ Fully end-to-end encryption from the client to the Internet destination
✗ Complete anonymisation
✗ Fully protect the privacy of access records
- What factors should be considered when choosing a personal VPN service?
There are a variety of free and paid personal VPN services on the market. Users can choose service providers carefully according to the below principles:
- What is the reputation of the VPN service provider? Whether the VPN service provider is an unknown brand?
- Does the VPN service provider timely provide patch software when it discovers product vulnerabilities?
- Has VPN service provider ever experienced a major data breach incident?
- Does the VPN service provider specify user privacy policies?
- Do the terms of use or privacy policy clearly state the use of data, collection purpose, and usage restrictions and provide appropriate security protection measures?
- If the user requires a VPN server of specific regions, does the service provider provide?
- How to configure Personal VPN software properly?
The setting for VPN software varies from vendor to vendor. Here we list out some common features that you need to know when you configure your VPN software. We encourage you to read through the documentation provided by the vendor during the configuration.
- Enable strong authentication. In using personal VPN service, you need to authenticate with the VPN server. You should choose a strong password and enable multi-factor authentication if applicable;
- Select a secure VPN protocol. Different VPN protocols have different security properties and encryption strength. You should always choose secure VPN protocols such as OpenVPN and IKEv2 of IPSec[2] as far as possible;
- Enable “Send All Traffic via VPN” option. This can ensure all data will be sent to VPN server when VPN service is running;
- Enable “Automatic VPN Connection for Wi-Fi network” option. Whenever you join a Wi-Fi network, the personal VPN will be connected automatically and your traffic will be transmitted through an encrypted VPN tunnel to reduce the security risk in using public Wi-Fi;
- Enable “Kill-Switch” feature. It can prevent your device from transmitting information if the VPN becomes disconnected;
- Enable “DNS mode via VPN” option. This can ensure that you are using the DNS setting provided by your personal VPN provider, so as to prevent your IP address or network access information is leaked due to DNS query; and
- Keep your VPN client software version up-to-date. This can highly reduce the risk due to known vulnerabilities and software bugs.
- VPN Security Test
After connecting to the server of the personal VPN service provider, you can first conduct the following VPN security tests to ensure that there are no hidden security risks before connecting to the Internet:
7.1 DNS leak test
DNS leak means that DNS queries are sent outside the VPN encrypted tunnel, the main reason is that the VPN service is incorrectly configured on the device. Users can use free online tools to test, for example: https://dnsleaktest.com/ .
7.2 IP address leak test
To ensure that the IP address is hidden, users can use free online tools to test, such as: https://ipleak.org/ .
7.3 WebRTC leak test
WebRTC is an API that is mainly used in web browsers such as Firefox, Chrome and Opera. It allows file sharing, voice and video chat within the browser. However, when the browser uses the WebRTC API, the user's IP address may leak out. Users can disable WebRTC in the browser to prevent its leakage. You can also use online tools for testing, such as: https://www.expressvpn.com/webrtc-leak-test .
- Conclusion
Although the personal VPN service does not provide complete anonymisation and peer-to-peer encrypted transmission from the client to the Internet destination, as long as you choose a reliable personal VPN service provider and properly configure the VPN software, for example, using two-factor authentication and secure protocol, then you can greatly increase your privacy level when using the public network.
If business users want to know more about the information regarding the use of remote security tools, please refer to HKCERT's security guideline "Assessing the Security of Remote Access Services Guideline".
[1] 7 VPN services leaked data of over 20 million users, says report
https://www.welivesecurity.com/2020/07/20/seven-vpn-services-leaked-data-20million-users-report/
[2] Guide to IPsec VPNs (NIST.SP.800-77r1)
https://csrc.nist.gov/publications/detail/sp/800-77/rev-1/final
Share with
