Hong Kong Security Watch Report (Q1 2014)
HKCERT is pleased to bring to you the "Hong Kong Security Watch Report" for the first quarter of 2014.
Nowadays, a lot of “invisible” compromised computers are controlled by attackers with the owner being unaware. The data on these computers may be mined and exposed everyday and the computers may be utilized in different kinds of abuse and criminal activities.
The Hong Kong Security Watch Report aims to provide the public a better “visibility” of the situation of the compromised computers in Hong Kong so that they can make better decision in protecting their information security.
The report provides data about the activities of compromised computers in Hong Kong which suffer from, or participate in various forms of cyber attacks, including web defacement, phishing, malware hosting, botnet command and control centres (C&C) and bots. Computers in Hong Kong is defined as those whose network geolocation is Hong Kong, or the top level domain of their host name is “.hk” or “.香港”.
Highlight of Report
This report is for Quarter 1 of 2014.
In this period, there were 15,235 unique security events related to Hong Kong used for analysis in this report. The information is collected with IFAS1 from 19 sources of information2. They are not from the incident reports received by HKCERT.
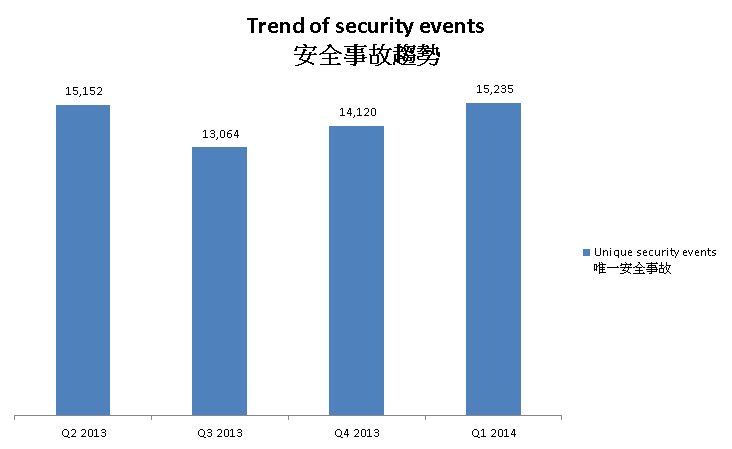
Figure 1 –Trend of security events
Server related security events
Server related security events include malware hosting, phishing and defacement. Their trend and distribution is summarized below:
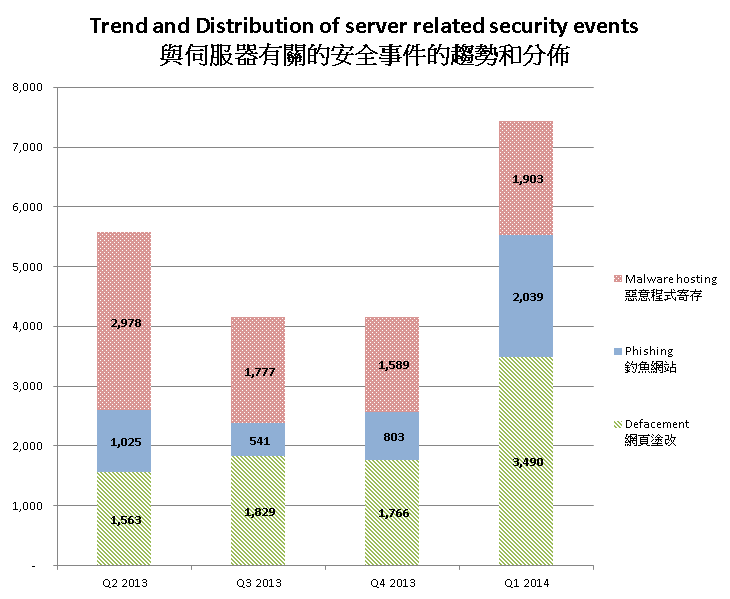
Figure 2 –Trend and distribution of server related security events distributions
The number of server related security events significantly increased in Q1 2014.
In this quarter, the number of malware hosting security events had increase of 20% while the number of phishing and defacement increased significantly, by 154% and 97% respectively.
The number of malware hosting and defacement showed a sharp increase in March. The number of malware hosting was increased by 227% in March 2014. The number of phishing showed a sharp increase by 62% in January and kept the increasing trend through the whole quarter.
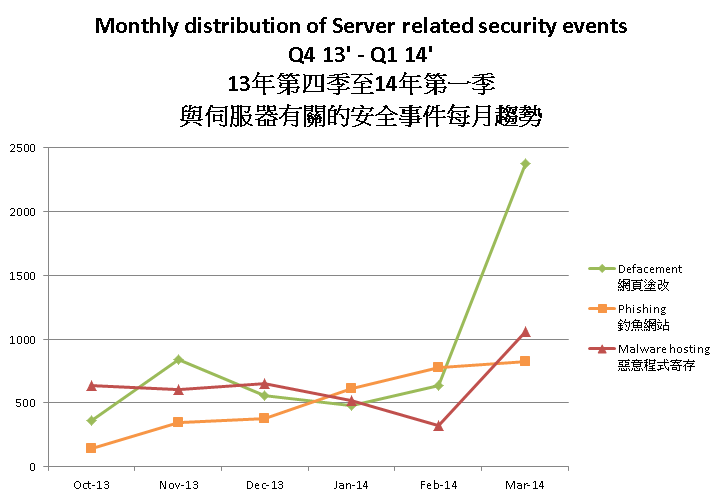
Figure 3 Monthly Distribution of Server Related Security Events Q4 13' - Q1 14'
The growth in number of server related security events is alarming. The numbers implies there were lots of traps on the Internet serving malicious activities. In other words, users might be at risks when visiting the vulnerable websites.
Recent study showed that some of the exploited servers were not compromised by attacks against their vulnerabilities or misconfigurations; but by theft of the administrators’ credentials. Security researchers pointed out that “while anti-virus and two factor authentication is common on the desktop, it is rarely used to protect servers, making them vulnerable to credential stealing and easy malware deployment."
| HKCERT urges system and application administrators to protect the servers. |
|
Botnet related security events
Botnet related security events can be classified into two categories:
- Botnet Command and Control Centres (C&C) security events – involving small number of powerful computers, mostly servers, which give commands to bots
- Bots security events – involving large number of computers, mostly home computers, which receive commands from C&C.
Botnet Command and Control Servers
The trend of botnet C&C security events is summarized below:
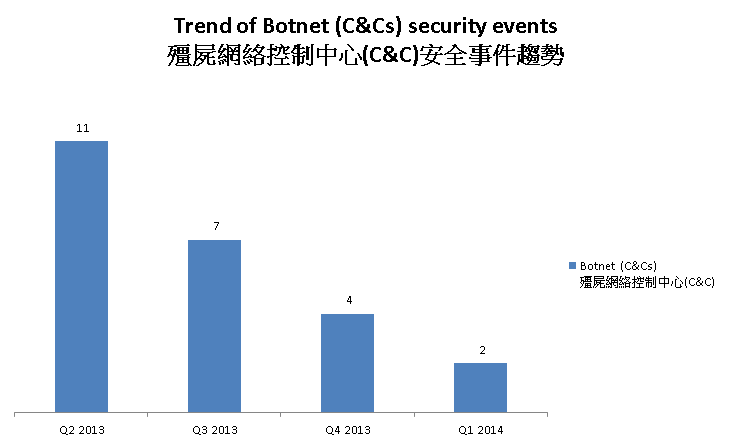
Figure 4 –Trend of Botnet (C&Cs) related security events
Number of botnet Command and Control Servers was decreasing across the four quarters.
There were 2 C&C servers reported in this quarter. One of the reported servers were identified as Zeus C&C servers, while the other was IRC bot C&C servers.
The trend of botnet (bots) security events is summarized below:
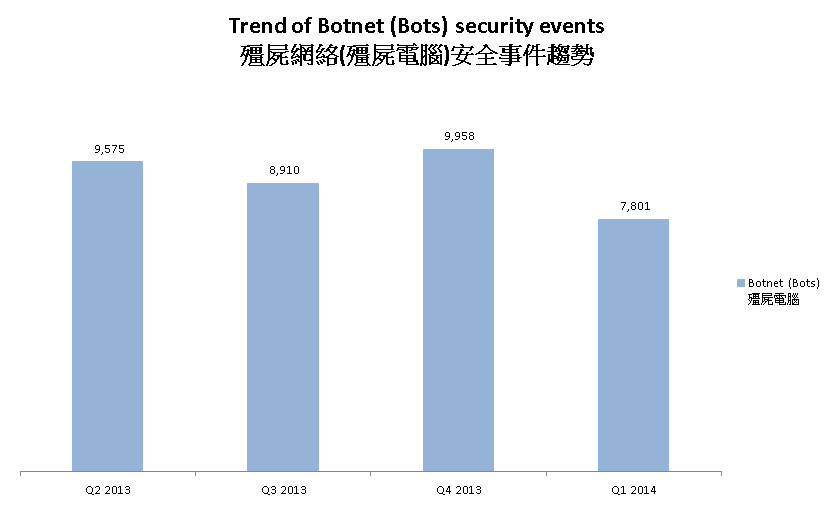
Figure 5 - Trend of Botnet (Bots) security events
Number of Botnet (bots) on Hong Kong network decreased in this quarter.
In Q1 2014, the number of botnet infection in Hong Kong decreased by 21.7%. Nine out of the top ten botnet showed a decrease in infection number. Among which, Pushdo showed the most significant decrease of 51.24%.
HKCERT has been following up the security events received and proactively engaged local ISPs for the botnet clean up since June 2013. Currently, botnet cleanup operations against major botnet family - Pushdo, Citadel and ZeroAccess are in action.
| HKCERT urges users to protect computers so as not to become part of the botnets. |
|
Among all the botnet family, Zeus has brought to our attention since Q4 2013. Zeus botnet security events in Oct 2013 had started to grow, and continued to soar through Q1 2014 despite a marginal drop in February 2014. It implied that Zeus botnet had been active or more users were infected with Zeus.
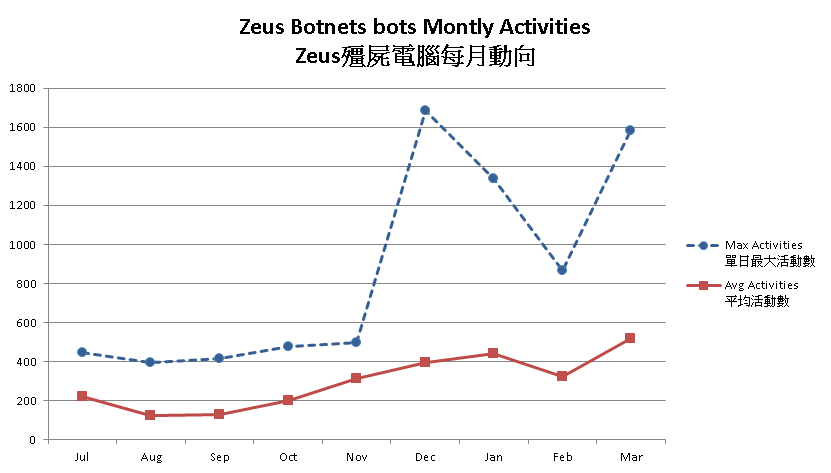
Figure 6 - Zeus Botnets Bots Monthly Activities
One of the reasons may be Zeus was being use to download the recent infamous ransomeware – Cryptolocker . Security researchers observed a connection between Zeus botnet and Cryptolocker. The Cutwail-UPATRE-ZEUS-CRILOCK infection chain was believed to be the most common ways to spread Cryptolocker . Also, with the arrest of the author of BlackHole Exploit Kit, “Paunch”, in October 2013, researchers observed the kit was replaced by the Cutwail-UPATRE-ZEUS-CRILOCK infection chain. It also leads to an increase of Zeus botnet.
Besides acting as downloader of other malware, Zeus is a famous financial trojan. It was designed to steal confidential information, e.g. target system information, online credential, bank details. Recently, news reported that the attacks by Zeus botnet are not only against financial institutions, but also against websites and services with ample of personal information. For example, the attack detected against Salesforce.com , a widely adopted CRM platform, in Feb 2014, and attacks against famous recruitment websites, Monster.com and Careerbuilder.com in March 2014.
HKCERT urges general users to join the cleanup acts. Ensure your computers are not being infected and controlled by malicious software.
Protect yourself and keep the cyberspace clean.
| Users can use the HKCERT guideline to detect and clean up botnets |
|
Download Report
< Please click to download Hong Kong Security Watch Report >
1Information Feed Analysis System (IFAS) is a HKCERT developed system that collects global security intelligence relating to Hong Kong for analysis.
Share with


