Best Practice Guide of Remote Desktop (for corporate administrator)
Remote Desktop is a useful tool for remote control a computer, but misconfigured Remote Desktop is risky. Using weak password to protect Internet accessible remote desktop and sharing password to the technical support vendor are some of these examples. They could lead to server being compromised or even infected with ransomware. To cope with evolving cyber security risks, secure the Remote Desktop is essential nowadays.
Part A: General best practices
- Disable Remote Desktop if it is unnecessary.
- Configure Account Lockout Threshold
- Configure Password Policy (password complexity, length, age and history)
- Restrict IP for remote access
- Use non-default port for remote desktop
- Adopt least privilege principle for the remote desktop user
- Use VPN or multi-factors authentication to protect Remote Desktop
Part B: Detail steps
Prerequisites
- Administrator should have basic knowledge on Windows server administration e.g. Group Policy configuration, firewall configuration etc.
- Administrator should fully review your environment and requirements before applying these practices, some of them may be inapplicable to your environment or only applicable partially. e.g. The Remote Desktop service is necessary for some servers, therefore “Disable Remote Desktop” is inapplicable for the whole domain.
- Administrator privilege is required for implementation of best practices.
- Be cautious, misconfiguration may lead to an unfavorable situation e.g. service interruption or failed security restriction, use it at your own risk. e.g. test it in the UAT site first.
- Disable Remote Desktop if it is unnecessary.
- Configure Account Lockout Threshold, to prevent password Brute-force attack.
- Configure Password Policy, to reduce risks from the password Brute-force attack.
- Configure Password Policy, to reduce risks from the password Brute-force attack.
- Configure Password Policy, to enforce change password regularly.
- Configure Password Policy, to prevent reuse recent passwords.
- Restrict IP for remote access : Configure firewall rule, to allow particular IP to remote desktop
- Use non-default port for remote desktop : Configure listen port for remote desktop
Configure via Group Policy:
Computer Configuration-> Policies-> Administrative Templates-> Windows Components -> Remote Desktop Services -> Remote Desktop Session Host -> Connections -> Allow users to connect remotely by using Remote Desktop Services
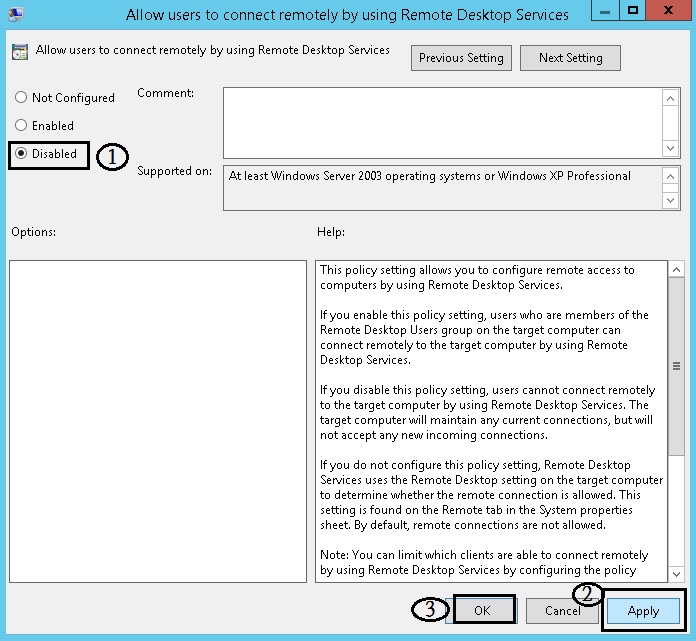
Configure via Group Policy:
Computer Configuration-> Policies-> Windows Settings-> Security Settings-> Account Policies-> Account lockout threshold
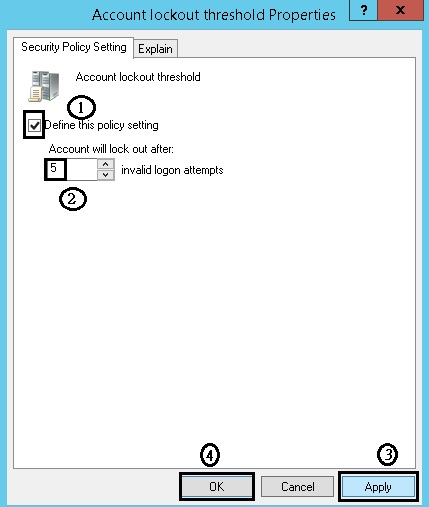
Configure via Group Policy:
Computer Configuration-> Policies-> Windows Settings-> Security Settings-> Account Policies-> Password Policy->Password must meet complexity requirements
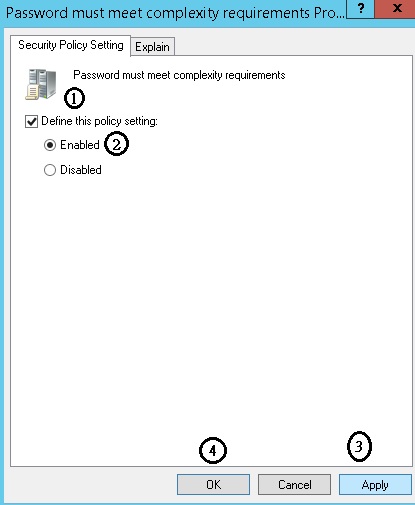
Configure via Group Policy:
Computer Configuration-> Policies-> Windows Settings-> Security Settings-> Account Policies-> Password Policy->Minimum password length
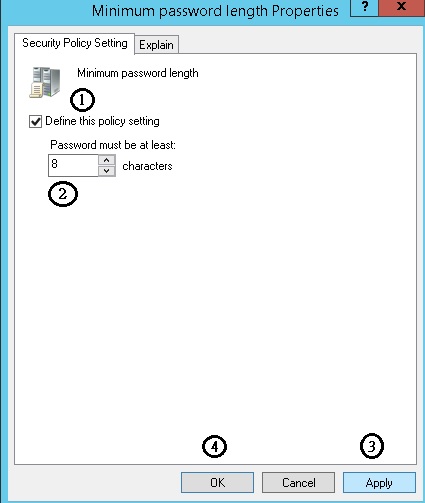
Configure via Group Policy:
Computer Configuration-> Policies-> Windows Settings-> Security Settings-> Account Policies-> Password Policy->Maximum password age
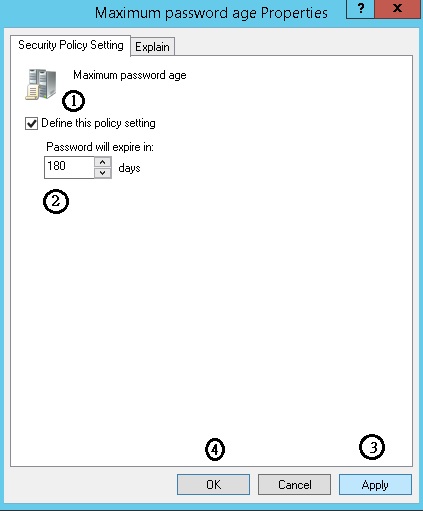
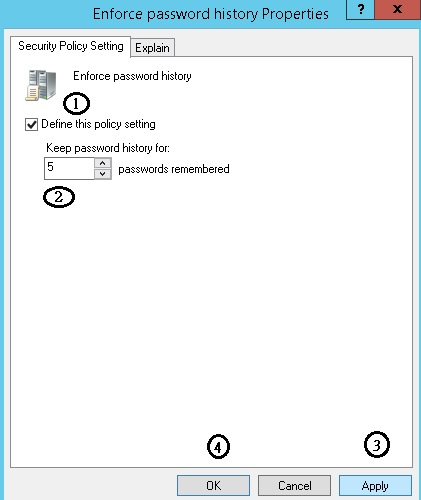
Configure via Group Policy:
Computer Configuration-> Policies-> Windows Settings-> Security Settings-> Account Policies-> Password Policy->Enforce password history
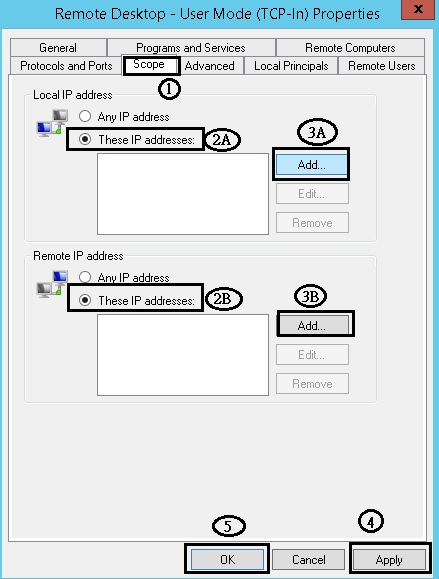
Configure via “Windows firewall with advanced security” :
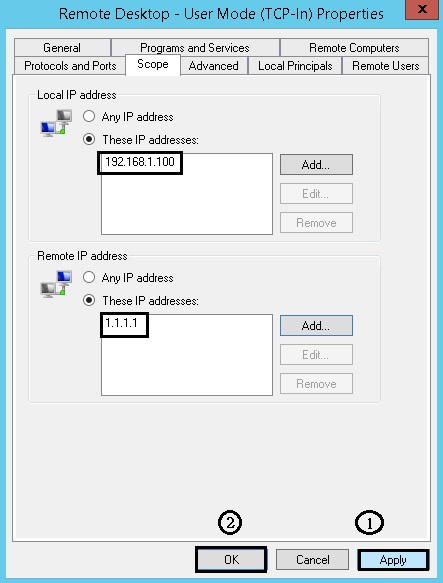
Remote Desktop - User Mode (TCP-In)
Assume that this firewall rule is an “Allow” rule, specify the IP address(es) that can remote desktop to this server. In this example, 192.168.1.100 and 1.1.1.1 are allowed IP.
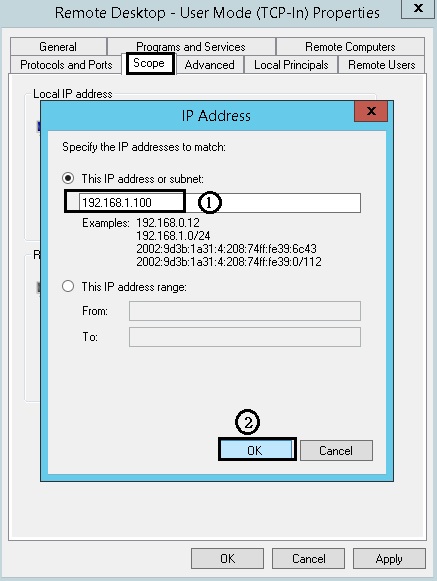
Configure via “Registry Editor” :
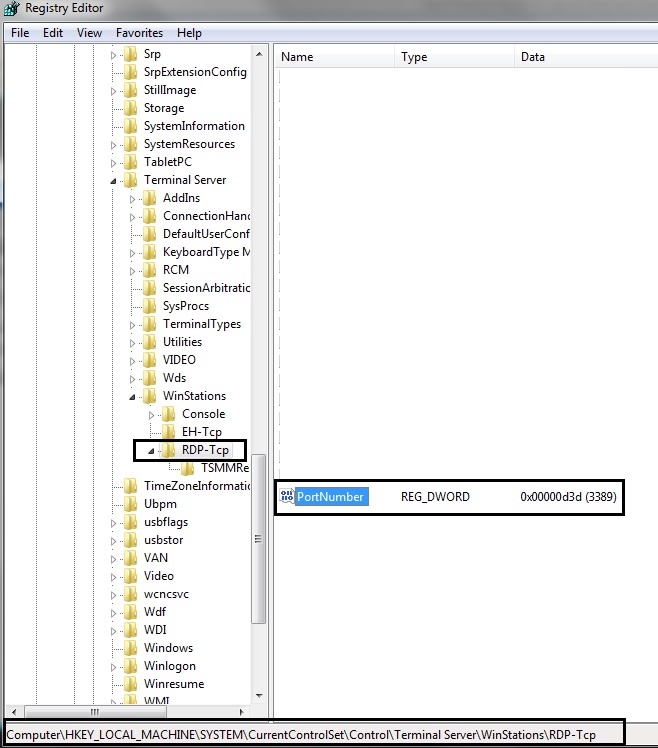
run "regedit" >
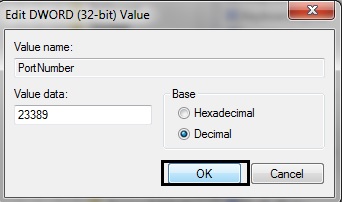
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\TerminalServer\WinStations\RDP-Tcp\PortNumber > right click and select modify > select "Decimal" in the Base, you should see the Value data is "3389", then change it to the other port number e.g. 23389 and click ok.
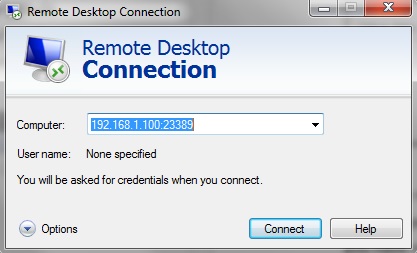
Please be reminded that you should define a firewall rule (e.g. Windows Firewall) for this new port in order to enable user to remote desktop via this new port. The new port is effective once you have rebooted the server. The example below showed that how to remote to the new port 23389.
After implementation of these best practices for Remote Desktop, organizations can mitigate related risks from Remote Desktop. To further secure Remote Desktop, HKCERT suggests organization may consider to adopt least privilege principle for the remote desktop user and use VPN or multi-factors authentication to protect Remote Desktop.
Share with
